

Find out how blockchain technology works, what makes cryptocurrencies so popular, and why Bitcoin is so volatile.
Let’s start with the basics; what is blockchain? We’re starting here because this technology is at the heart of many cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin. What’s more, the uses of blockchain technology go far beyond just digital currencies.
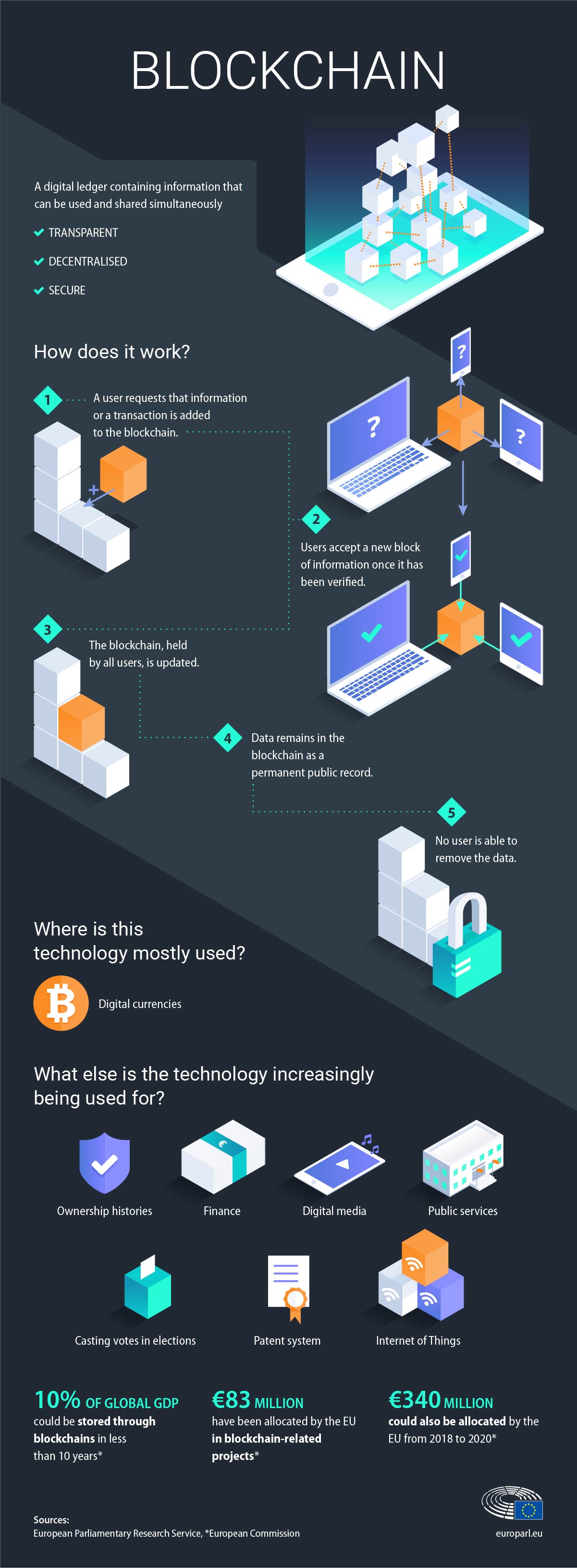
In the simplest terms, a blockchain is a type of database – a collection of electronically stored information or data. Yet a blockchain has many unique features that make it different from a traditional database. As the name suggests, a blockchain is a series of data ‘blocks’ that are linked together. This chain of blocks creates a shared digital ledger (collection of data) that records the activity and information within the chain.
Each blockchain ledger is stored globally across thousands of different servers. This means that anyone on the network can see (and verify) everyone else’s entries. This peer-to-peer and distributed ledger technology, as it’s known, means that it’s nearly impossible to falsify or tamper with data within a block.
So, to use IBM’s definition, blockchain is a shared, immutable (permanent and unalterable) ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets.
We now know what a blockchain is, but how does the technology work? We’ll keep things at a basic level here.
Website Designed by Piyush Mohapatra